A’dark factory“, in which new cars are manufactured entirely by robots without human intervention, is expected to open as early as 2030 and revolutionize vehicle construction, according to analysts.
In what could be the biggest shakeup since Ford’s introduction of the moving assembly line to produce the Model T in 1913 – cutting production times and costs while lowering showroom prices – the “dark factory” will have serious implications beyond the factory floor.
Accordingly Automotive NewsThe move could transform vehicle design principles, workforce training and the economics of car manufacturing through faster model changes.
It cites a McKinsey study suggesting that integrating robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) into manufacturing could create US$150 billion (AU$223 billion) in annual “economic potential”.
With Daily Sparkz you can save thousands on a new car. Click Here to get a great deal.
Advantages on the factory floor include a robot’s ability to change tasks and perform processes impossible for humans while not suffering from fatigue – or, as was the case with Ford in the 1910s, boredom from repetitive tasks.
These factors also reduce the likelihood of errors compared to human production workers, thereby improving manufacturing efficiency and the quality of the finished vehicle.
The use of robotics in vehicle production and development is anything but new.
Ford Australia even used robot test drivers in the development of its Ranger Super Duty ute, which went on sale late last year.
Nevertheless, humanoid robots are increasingly becoming the focus of vehicle production, which is expected to culminate in the first “dark factory”.
Analysts from technology firm Gartner and Warburg Research said Automotive News Several major automotive companies are “already setting up disruptive manufacturing processes and placing a greater focus on humanoid robots.”
At least a dozen leading automakers are testing advanced robotics in their factories, and a fully robotized “dark factory” is likely to open by “the end of this decade,” according to Pedro Pacheco, vice president of research at Gartner.
“Recognizably, they don’t have much impact on vehicle assembly at the moment. However, it is likely that their capabilities will continue to develop over the course of this decade, given how focused so many automakers are on this,” Pacheco said.
This is what Gartner analyst Marco Sandrone said Automotive News The only parts of the vehicle manufacturing process that are not fully automated are the installation of wiring harnesses and interior components.
Companies in the automotive supply chain with published plans to use humanoid robots include Tesla and BYD.
BMW has already worked with robotics company Figure AI. The company said in November that after an 11-month deployment of its Figure 02 robot, it had loaded 90,000 parts in 10-hour shifts five days a week and helped produce over 30,000 X3s.
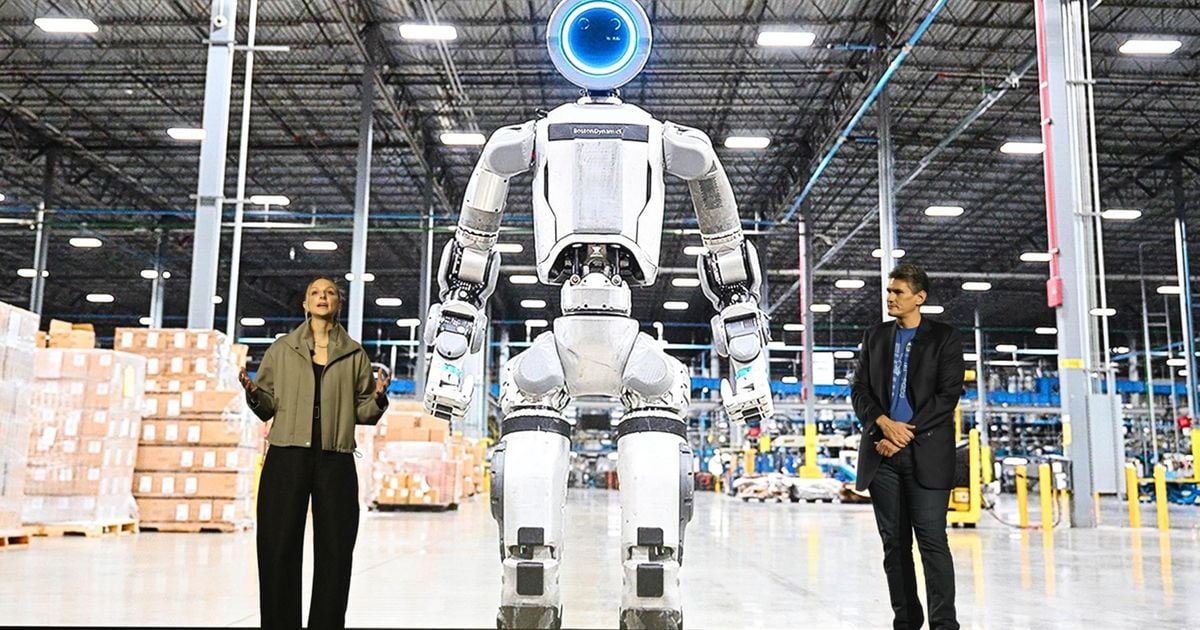
Hyundai plans to use its Boston Dynamics robots at its plant in Georgia, USA, from 2028.
Earlier this month, the company introduced its humanoid robot “Atlas” at the Consumer Electronics Show (CES) in Las Vegas and said it “plans to integrate Atlas into its global network.”
Hyundai Motor Group (HMG) bought an 80 percent stake in Boston Dynamics in 2021, saying the two companies were working on a “robotics value chain” to build cars faster while ensuring safety.
The Korean automaker said robots offer “opportunities for rapid growth and the potential to have a positive impact on society by making work safer and more productive.”
Robots are already in use at Hyundai’s electric vehicle “smart factory” in Singapore, which opened in 2023 “integrating people, robotics and AI technology.”
Mercedes-Benz is testing humanoid robots in its factories and announces that its “Apollo” robots from Apptronik will interact with humans in 2025.
“Around 2030 we will see at least some humanoid robots in production,” said the automaker’s head of production, Jörg Burzer.
MORE: Chery is almost ready to let AI design its next car